人工智能竞赛-目标识别指导

本文为看雪论坛优秀文章
看雪论坛作者ID:pureGavin
一
前言
二
前置小知识
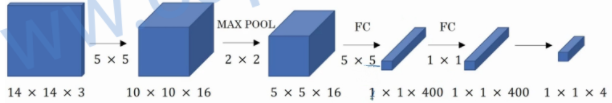
三
我的代码
yolo介绍

代码部分
import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tfimport cv2from IPython.display import Image,displayfrom tensorflow.keras.models import load_modelfrom yolo_utils import read_classes,read_anchors,yolo_head,preprocess_image,generate_colors,draw_outputs%matplotlib inline
################################################################################################ 过滤概率低的边框# 参数:# box_confidence:装载着每个边框的pc# boxes:装载着每个边框的坐标# box_class_probs:装载着每个边框的80个种类的概率# threshold:阈值,概率低过这个值的边框会被过滤掉## 返回值:# scores:装载保留下的那些边框的概率# boxes:装载保留下的那些边框的坐标# classes:装载保留下的那些边框的种类的索引###############################################################################################def yolo_filter_boxes(box_confidence,boxes,box_class_probs,threshold=.6):# 将pc和c相乘,得到具体某个种类是否存在的概率box_scores=box_confidence*box_class_probs# 获取概率最大的那个种类的索引box_classes=tf.argmax(box_scores,axis=-1)# 获取概率最大的那个种类的概率值box_class_scores=tf.reduce_max(box_scores,axis=-1)# 创建一个过滤器,当某个种类的概率值大于等于阈值时,对应这个种类的filtering_mask中的位置就是true,否则就是false# filtering_mask就是[false,true,...,false,true]这种形式filtering_mask=tf.greater_equal(box_class_scores,threshold)# 用上面的过滤器过滤掉那些概率小的边框# 过滤完成后,scores和boxes,classes里面就只装载了概率大的边框的概率值和坐标以及种类索引了scores=tf.boolean_mask(box_class_scores,filtering_mask)boxes=tf.boolean_mask(boxes,filtering_mask)classes=tf.boolean_mask(box_classes,filtering_mask)return scores,boxes,classes# 模块测试box_confidence=tf.random.normal([13,13,3,1],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1)boxes=tf.random.normal([13,13,3,4],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1)box_class_probs=tf.random.normal([13,13,3,80],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1)scores,boxes,classes=yolo_filter_boxes(box_confidence,boxes,box_class_probs,0.5)print("scores[2]=",scores[2])print("boxes[2]=",boxes[2])print("classes[2]=",classes[2])print("scores.shape=",scores.shape)print("boxes.shape=",boxes.shape)print("classes.shape=",classes.shape)
################################################################################################ 用非最大值抑制技术过滤掉重叠的边框# 参数:# scores:前面yolo_filter_boxes函数保留下的那些边框的概率值# boxes:前面yolo_filter_boxes函数保留下的那些边框的坐标# classes:前面yolo_filter_boxes函数保留下的那些边框的种类的索引# max_boxes:最多想要保留多少个边框# iou_threshold:交并比阈值,交并比大于这个阈值的边框才会被进行非最大值抑制处理## 返回值:# scores:NMS保留下的那些边框的概率# boxes:NMS保留下的那些边框的坐标# classes:NMS保留下的那些边框的种类的索引###############################################################################################def yolo_non_max_suppression(scores,boxes,classes,max_boxes=20,iou_threshold=0.5):# NMS函数,此函数会返回NMS后保留下来的边框的索引nms_indices=tf.image.non_max_suppression(boxes,scores,max_boxes,iou_threshold=iou_threshold)# 通过上面的索引来分别获取被保留的边框的相关概率值、坐标以及种类的索引scores=tf.gather(scores,nms_indices)boxes=tf.gather(boxes,nms_indices)classes=tf.gather(classes,nms_indices)return scores,boxes,classes# 模块测试scores=tf.random.normal([54,],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1)boxes=tf.random.normal([54,4],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1)classes=tf.random.normal([54,],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1)scores,boxes,classes=yolo_non_max_suppression(scores,boxes,classes)print("scores[2]=",scores[2])print("boxes[2]=",boxes[2])print("classes[2]=",classes[2])print("scores.shape=",scores.shape)print("boxes.shape=",boxes.shape)print("classes.shape=",classes.shape)
################################################################################################ 最终的过滤函数# 参数:# yolo_outputs:YOLO模型的输出结果# max_boxes:你希望最多识别出多少个边框# score_threshold:概率值阈值# iou_threshold:交并比阈值## 返回值:# scores:最终保留下的那些边框的概率# boxes:最终保留下的那些边框的坐标# classes:最终保留下的那些边框的种类的索引###############################################################################################def yolo_eval(outputs,max_boxes=20,score_threshold=0.5,iou_threshold=0.5):# 建立3个空lists,b,c=[],[],[]# 后面调用的Yolov3使用了3个规格的网格(13*13,26*26,52*52)进行预测,所以有三组outputfor output in outputs:# 将YOLO输出结果分成3份,分别表示概率值、坐标、种类索引box_confidence,boxes,box_class_probs=output# 使用之前实现的yolo_filter_boxes函数过滤掉概率值低于阈值的边框scores,boxes,classes=yolo_filter_boxes(box_confidence,boxes,box_class_probs,threshold=score_threshold)s.append(scores)b.append(boxes)c.append(classes)# 将3组output的结果整合到一起scores=tf.concat(s,axis=0)boxes=tf.concat(b,axis=0)classes=tf.concat(c,axis=0)# 使用yolo_non_max_suppression过滤掉重叠的边框scores,boxes,classes=yolo_non_max_suppression(scores,boxes,classes,max_boxes=max_boxes,iou_threshold=iou_threshold)return scores,boxes,classesyolo_output=(tf.random.normal([13,13,3,1],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1),tf.random.normal([13,13,3,4],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1),tf.random.normal([13,13,3,80],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=1))yolo_output1=(tf.random.normal([26,26,3,1],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=2),tf.random.normal([26,26,3,4],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=2),tf.random.normal([26,26,3,80],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=2))yolo_output2=(tf.random.normal([52,52,3,1],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=3),tf.random.normal([52,52,3,4],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=3),tf.random.normal([52,52,3,80],mean=1,stddev=4,seed=3))# 模块测试yolo_outputs=(yolo_output,yolo_output1,yolo_output2)scores,boxes,classes=yolo_eval(yolo_outputs)print("scores[2]=",scores[2])print("boxes[2]=",boxes[2])print("classes[2]=",classes[2])print("scores.shape=",scores.shape)print("boxes.shape=",boxes.shape)print("classes.shape=",classes.shape)
# 定义种类已经anchor box和像素class_names=read_classes("model_data/coco_classes.txt")anchors=read_anchors("model_data/yolo_anchors.txt")# 加载已经训练好的YOLO模型yolo_model=load_model("model_data/yolo_model.h5")yolo_model.summary()
# 探测图片img_raw,img=preprocess_image("test.jpg",model_image_size=(416,416))yolo_outputs=yolo_model(img)# 将YOLO模型的输出结果转换成我们需要的格式outputs=yolo_head(yolo_outputs,anchors,len(class_names))# 过滤边框out_scores,out_boxes,out_classes=yolo_eval(outputs)
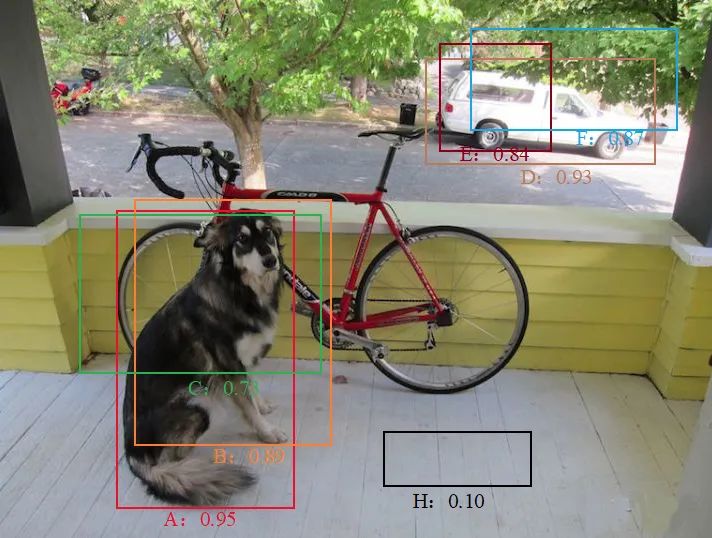
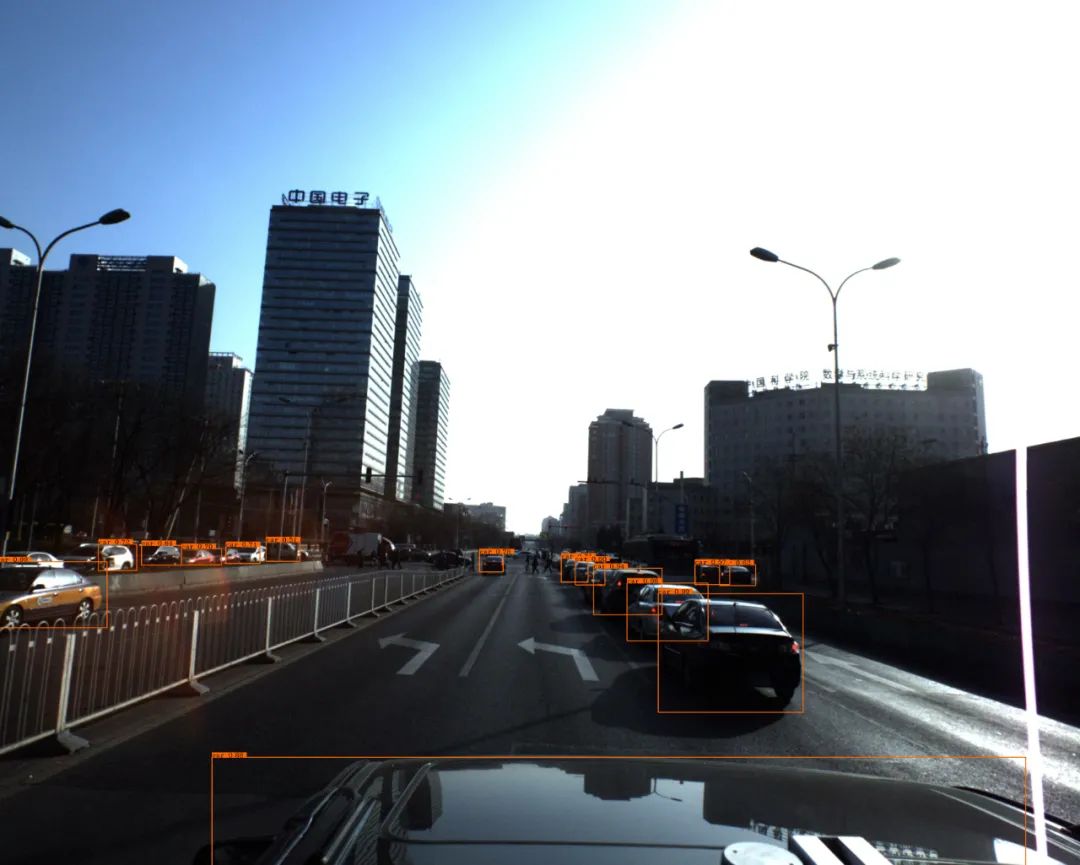
# 加载图片并进行测试def img_show(image_file,out_scores,out_boxes,out_classes,class_names):img_raw=tf.image.decode_image(open('./images/'+image_file,'rb').read(),channels=3)img=cv2.cvtColor(img_raw.numpy(),cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)colors=generate_colors(class_names)# print('在{}图片中找到{}个目标'.format(image_file),len(out_boxes))print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes),image_file))img=draw_outputs(img,out_scores,out_boxes,out_classes,colors,class_names)display(Image(data=bytes(cv2.imencode('.jpg',img)[1]),width=800))file_name=[x for x in image_file.split('.')]cv2.imwrite('./res/'+file_name[0]+'_out.'+file_name[1],img)return img# 使用测试训练集进行检测img=img_show('test.jpg',out_scores,out_boxes,out_classes,class_names)

# 对目标图片进行预测def predict(model,image_file,anchors,class_names):img_raw,img=preprocess_image(image_file,model_image_size=(416,416))yolo_outputs=yolo_model(img)outputs=yolo_head(yolo_outputs,anchors,len(class_names))out_scores,out_boxes,out_classes=yolo_eval(outputs)img=img_show(image_file,out_scores,out_boxes,out_classes,class_names)return imgimg=predict(yolo_model,'ID_6ae2b25af.jpg',anchors,class_names)

import osEpath=os.walk('./images')for path,dir,filelist in Epath:for filename in filelist:img_path = os.path.join(filename)#print(img_path)img=predict(yolo_model,img_path,anchors,class)
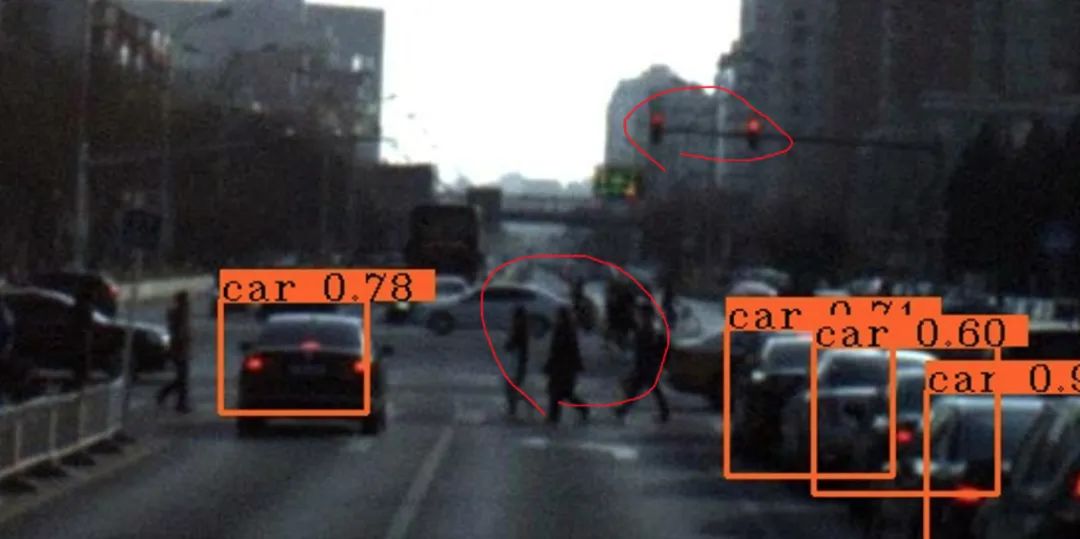

四
结束语
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/76802514
https://www.jianshu.com/p/043966013dde
https://www.cnblogs.com/chenhuabin/p/13908615.html

看雪ID:pureGavin
https://bbs.pediy.com/user-home-777502.htm

# 往期推荐
4.Windows本地提权漏洞CVE-2014-1767分析及EXP编写指导
6.高级进程注入总结
球分享

球点赞

球在看
点击“阅读原文”,了解更多!
[广告]赞助链接:
关注数据与安全,洞悉企业级服务市场:https://www.ijiandao.com/
让资讯触达的更精准有趣:https://www.0xu.cn/
 关注KnowSafe微信公众号
关注KnowSafe微信公众号随时掌握互联网精彩
- AgentScope通义实验室开源的multi-agent编程框架
- GoAccess开启高效网络日志分析
- 第一款月活破亿的短剧APP诞生:用户暴增10倍!
- 自增id和uuid的优劣 为什么要用自增ID
- Linux 的成功,为什么会带来“写一个操作系统不难,难的是生态构建”的错觉?
- 高通推出第一代骁龙6和第一代骁龙4移动平台,将旗舰特性下沉带给更多消费者
- 肆意赋红码,按“数安法”该当何罪?
- 儿童节 | 科技小学堂 让科技梦想在每一个孩子心中放飞
- 登陆官网即可领取万元豪礼,还不快来!
- 做个“原年人”,过个“幸福年”,又拍云送福利啦!
- 高朋满座话未来|专访realme创始人兼CEO李炳忠
- 诸子云 | POC第一期:11家甲方实测4家乙方产品
赞助链接